Product introduction
Bailey Bridge Rock: used to control the direction of the truss push out and bear the weight of the bridge. A semi-crescent shim iron is arranged under it, which is convenient to be supported on the axle beam of the bridge seat. The rock can swing up and down freely. There are 4 small rollers on both sides. When pushing and pulling the bridge span, the lower chord of the truss is always controlled in the center of the rock to ensure the direction of pushing and pulling the bridge span. Rock and roll should be set up on both sides of the strait. The rock weighs 102 kilograms and the maximum load-bearing capacity is 250 kN.
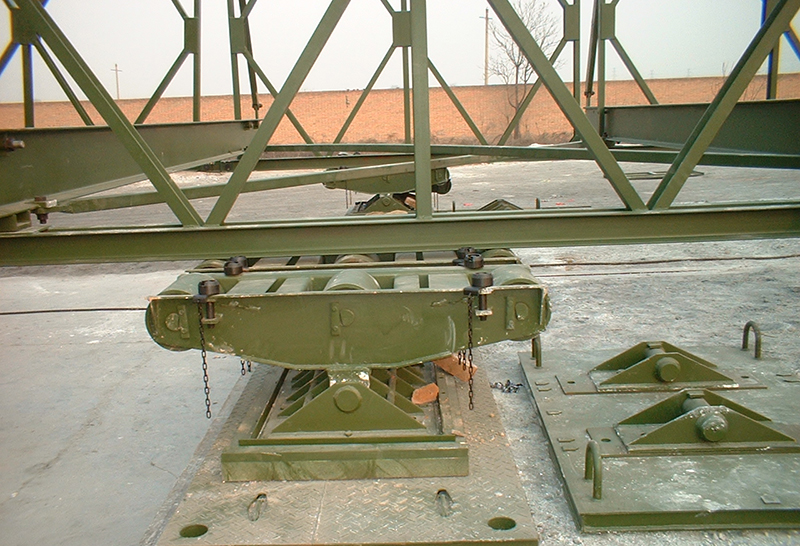
Application
The vertical slope of the assembled site should not be greater than 3%, and the horizontal slope should be roughly horizontal. Set the roller at the position of the calibrated roller, and the sample tray should be placed underneath. Each rock only allows one row of trusses to pass. When a single-row bridge is erected, two rockers are set on each bank; when two-row and three-row bridges are erected, four rockers are set on each bank. When pushing the three rows of bridges, in order to avoid obstructing the smooth passage of the outer row of trusses, the outer rollers under the middle row should be removed. The distance between the rock and the support plate is about 1.0 m, and at least not less than 0.75 m. The seat plate is set at the position of the seat plate axis. Since the bridge deck is 79 cm higher than the bottom surface of the seat plate, the seat plate position should be properly excavated to reduce the elevation of the bridge deck. Generally, the height difference between the bridge deck and the road surface should not exceed 30 cm.









